Archive
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “Interchain Messaging”
In this course, you will learn how to build cross-L1 Solidity dApps with Interchain Messaging and Avalanche Warp Messaging.
Course Content
Interoperability
In the first section, we cover some basic concepts of interoperability in multi-chain systems. You will learn about examples of interoperability between blockchains and the terms “source,” “destination,” and “message.”
Avalanche Interchain Messaging
In this section, we learn what Avalanche Interchain Messaging is and what is abstracted away from the general dApp developer. You will also build your first cross-L1 dApps.
Securing Cross-Chain Communication
In this section, we look at techniques to secure cross-chain communication. We dive into signature schemes, multi-signature schemes, and the BLS multi-signature scheme.
Avalanche Interchain Messaging Protocol
Avalanche blockchains can natively interoperate between one another using AWM. You will learn about the AWM message format and how the message flow works.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, students will:
- Understand the challenges of cross-chain communication
- Know what separates Avalanche Warp Messaging from other cross-chain communication protocols
- Understand the differences between Avalanche Warp Messaging and Teleporter
- Apply their knowledge by building cross-Avalanche L1 dApps, such as asset bridges
Topics
- Interoperability between blockchain
- Source, Message and Destination
- Recap of Multi-Chain Networks
- Interoperability in Multi-Chain Systems
- Finality Importance in Interoperabile Systems
- Trusted Third Parties
- Avalanche Starter Kit
- Initial Setup
- Close and Reopen Codespace
- Getting Test Tokens
- Contract Development with Foundry
- Interchain Messaging Basics
- ICM Basics
- Recap of Bytes, Encoding and Decoding
- Sending a Message
- Sender Contract
- Receiving a Message
- Receiver Contract
- Send a Message
- Adapt the contract
- Two-Way Communication
- Sender Contract
- Create the Sender Contract
- Receiver Contract
- Create the Receiver Contract
- Send a Roundtrip Message
- Adapt the Contracts
- Invoking Functions
- Encoding of multiple Values
- Create Simple Calculator Sender
- Create Simple Calculator Receiver
- Call simple Calculator
- Encoding the Function Name
- Extend the Calculator
- Interchain Messaging Registry
- How the ICM Registry works
- Interact with the ICM Registry
- Retrieving Interchain Messenger from the Registry
- Verify if Sender is Interchain Messaging
- Avalanche Warp Messaging
- Recap P-Chain
- Warp Message Format
- AWM Relayer
- Dataflow
- Message Pickup
- Message Delivery
- Load Considerations
- Trust Assumptions
- Running a Relayer
- Relayer Introduction
- Configuration Breakdown
- Configure & Run Relayer
- Restricting-the-relayer
- Restricting a Relayer
- Allowed Relayer
- Incentivizing a Relayer
- Incentivizing a Relayer
- Fee Data Flow
- Determining the Fee
- Setting Incentives
- Deploy Fee Token Contract
- Incentivize an AWM relayer
- Interaction Flow With Fees
Completion Certificate
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “Interchain Token Transfer”
In this course, you will learn how to transfer assets across multiple Avalanche blockchains with Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer ICTT.
Course Content
Getting Started with Interchain Token Transfer
In this section, you will learn how to use our Interchain Token Transfer toolbox to perform cross-chain operations. We’ll guide you through the process of using our user-friendly interface to deploy contracts, create bridges, and transfer assets across the testnet chains (Fuji C-Chain, Echo, and Dispatch).
Tokens and Token Types
In this section, you will learn about the different types of tokens that can be transferred between Avalanche blockchains. We will cover ERC-20 and native tokens and how to deploy and transfer them using our toolbox. Furthermore, you will learn what wrapped native tokens are and how they can be used to transfer assets between chains.
Token Bridging
Next we will talk about the high level concepts of token bridging and demonstrate how to use our toolbox to create and manage bridge contracts for cross-chain transfers between the testnet chains.
Interchain Token Transfer Architecture
In this chapter we will look at the design of Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer. You will learn about the file structure of the contracts and the concepts of the token home and token remote.
ERC-20 to ERC-20 Bridge Implementation
You will learn how to use our toolbox to deploy ERC-20 tokens and create bridges to transfer them between the testnet chains.
Multi-Chain Token Operations
Here you will learn about the concept of multi-hops and how to use our toolbox to bridge tokens between multiple testnet chains.
Native to ERC-20 Bridge Implementation
In this chapter you will learn how to use our toolbox to bridge a native token as an ERC-20 token to another testnet chain.
Send and Call Operations
In this chapter you will learn how to use our toolbox to call smart contracts with the tokens after sending them to another testnet chain.
Cross-Chain Token Swaps
In this chapter you will learn how to perform cross-chain token swaps between the testnet chains using our toolbox.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, you will:
- Understand what Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer is and when to use it.
- Understand the different options for transferring assets between multiple chains.
- Be able to deploy tokens and create bridges using our toolbox.
- Be able to perform cross-chain token transfers between testnet chains using our toolbox.
- Apply the knowledge gained in the course by enabling assets to be transferred between multiple Avalanche blockchains.
Topics
- Tokens
- Native Tokens
- Transfer Native Tokens
- Transfers and Smart Contract
- ERC-20 Tokens
- Deploy and Transfer an ERC-20 Token
- ERC-20 and Smart Contracts
- Wrapped Native Tokens
- Create a Wrapped Native Token
- Token Bridging
- Bridge Architecture
- Use a Demo Bridge
- Bridge Hacks
- Interchain Token Transfer
- Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer
- Interchain Token Transfer Design
- File Structure
- Token Home
- Token Remote
- ERC-20 to ERC-20 Token Bridge
- ERC-20 to ERC-20 Bridge
- Deploy an ERC-20
- Deploy a Home Contract
- Deploy a Remote Contract
- Register Remote Bridge
- Transfer Tokens
- Integrate ICTT with Core
- Deploy Your Own ICTT Frontend
- ERC-20 Multi-Hop Transfer
- Overview of Multi-hop Transfers
- Deploy Token Remote for Multi-hop
- Register Remote Bridge
- Multi-hop Transfer
- Native to ERC-20 Token Bridge
- Native to ERC-20 Token Bridge Overview
- Deploy Native Token Home
- Deploy ERC20 Token Remote
- Register Remote Bridge
- Native Token Bridge Transfer
- Send and Call
- Introduction
- Send and Call Receivers
- Mock Receivers
- Deploy a Mock Receiver
- Cross-Chain Token Swaps
- Wrap Exchange Contract
- Deploy Wrapped Exchange Contract
- Scaling Token Decimals
- Scaling with TokenRemote
- Example USDC as Native Token (DIY)
Completion Certificate
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “L1 Tokenomics”
This course is designed to give you a deep understanding of tokenomics, including the creation, distribution, utility, and governance of tokens within blockchain ecosystems. By the end of this course, you will have practical skills in managing tokens across multi-chain ecosystems, configuring transaction fees, and designing staking and governance models.
Course Content
Basics
Learn the fundamentals of tokenomics, including native tokens, ERC-20 tokens, wrapped tokens, and how token decimals affect transactions and supply.
Native Tokens
Explore how to create custom native tokens, use Avalanche’s native token minter, and integrate ERC-20 tokens as native tokens in cross-chain environments.
Multi-Chain Ecosystems
Delve into interchain token transfers and cross-chain functionality, using both ERC-20 and native tokens across multiple blockchains.
Staking
Understand staking tokens, liquid staking, and how to deploy staking contracts, with a focus on post-Etna upgrade features.
Transaction Fees
Master transaction fee configuration, dynamic fee models, and learn how to distribute fees effectively within decentralized ecosystems.
Token Distribution
Learn about initial token allocation, advanced vesting schedules, bonding curves for token pricing, and how to implement airdrops.
Governance
Study governance models, DAOs, quadratic voting, and the latest innovations in governance (Governance 2.0) for decentralized decision-making.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, you will:
- Gain a solid grasp of token fundamentals, tokenomics models, and how to create sustainable token economies.
- Learn how to create custom native tokens and integrate ERC-20 tokens as native tokens in multi-chain environments.
- Understand the challenges and opportunities in cross-chain token transfers, and liquidity management.
- Master the technical aspects of configuring transaction fees, setting up staking contracts, and designing dynamic fee models.
- Create initial allocation plans, implement advanced vesting schedules, and manage bonding curves and airdrops.
- Develop governance structures, including DAOs and quadratic voting models, to manage decentralized decision-making effectively.
Topics
- Basics
- Native Tokens
- ERC-20 Tokens
- Deploy and Transfer an ERC-20 Token
- Wrapped Native Tokens
- Deploy and Interact with Wrapped Token
- Token Decimals
- Advanced Native Tokens
- Custom Native Tokens
- Configure Custom Native Tokens
- Native Token Allocation
- Activating Native Minter Precompile
- Native Minter Precompile
- Use ERC-20 as Native Token
- Multi-Chain Ecosystems
- Introduction
- Interchain Token Transfers
- Use ERC-20 as Native Token (DIY)
- Use any Native as Native Token (DIY)
- Cross-Chain Liquidity Pools
- Quiz Time
- Staking
- Introduction
- Liquid Staking
- Staking Contract (post Etna Upgrade)
- Registering PoS Validators
- Transaction Fees
- Introduction
- Transaction Fee Configuration
- Dynamic Fee Configuration
- Fee Distribution
- Token Distribution
- Initial Allocation
- Vesting Schedules
- Bonding Curves
- Airdrops
- Governance
- Introduction
- Governance Models
- DAOs
- Quadratic Voting
- Governance 2.0
- Conclusion
Completion Certificate
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “Avalanche Fundamentals”
This online course introducing you to the exciting world of the Avalanche technology! This course will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the basic concepts making Avalanche unique.
Throughout, you’ll learn the key features and benefits of the platform, plus how to build on it. You can also ask our expert instructors questions.
By the end of these courses, you’ll have the knowledge and skills to leverage the power of blockchain technology for your own projects and applications. We’re excited to have you join us on this journey and can’t wait to see what you’ll create with Avalanche!
By the end of this course, you will:
- Understand how Avalanche consensus works and what makes it different.
- Understand how Avalanche L1s enable scalability, customizability, and independence.
- Understand the Primary Network, a special Avalanche L1, and how to interact with it.
- Understand how Virtual Machines enable developers to create more optimized and capable blockchain systems and to tackle completely new use cases unachievable with previous solutions.
You can evaluate your own understanding of the material through quizzes and claim a certificate for successful completion at the end.
Overall, this course aims to provide a foundational understanding of Avalanche. By completing it, you will be better prepared to take on more advanced courses focused on building on Avalanche.
Topics
- Avalanche Consensus
- Consensus Mechanisms
- Snowman Consensus
- Throughput vs. Time to Finality
- Multi-Chain Architecture
- Avalanche L1s
- Features & Benefits of Avalanche L1s
- Avalanche9000 Upgrade
- Avalanche L1s vs Layer 2
- Set Up Core Wallet
- Use Dexalot L1
- Creating an L1
- Connect & Fund Core Wallet
- Network Architecture
- Create a Blockchain
- Set up Validator Nodes
- Convert a Subnet to an L1
- Test your L1
- Remove Node
- Introduction in Interoperability
- Source, Message and Destination
- ICM, ICM Contracts & ICTT
- BLS Signature Schemes
- Use a Signature Scheme
- Multi-Signature Schemes
- Use Multi-Signature Schemes
- BLS Signature Aggregation
- Use Cases
- Introduction to VM Customization
- VM Configuration
- VM Modification
- VM Creation
- Permissioning
- Compliance
- Transaction Allowlist
- Activate Transaction Allowlist
- Contract Deployer Allowlist
- Activate Contract Deployer Allowlist
- Permissioning Validators
- Private Blockchains
- Intain Markets Case Study
CERTIFICATE OF COMPLETION
Cardano Academy
Cardano Academy
Certification “Cardano Blockchain Certified Associate” (CBCA)
Module 1 Overview
Introduces the foundation of blockchain, from the main components of a typical blockchain network, to how consensus algorithms provide a mechanism to reach agreement in decentralized systems. It delves into the Byzantine Generals’ Problem and explains what Byzantine and Practical Byzantine fault-tolerant systems are. This module looks at the key concepts behind proof-of-work and proof-of-stake systems, including their respective limitations. Other proof-based consensus models including proof of authority, proof of Importance and proof of History are briefly explored. Encryption methods are examined and how hash functions and digital signatures provide data authenticity and integrity.
Topics
- Introduction to Blockchain
- Consensus Algorithms
- The Byzantine Generals Problem (BGP)
- The Basics of Networks
- Properties of Consensus Algorithms
- The Original Bitcoin Whitepaper
- BFT vs. PoW Consensus Algorithms
- Blockchain Fundamentals
- Components and Structure of a Blockchain
- Blockchain Careers and Use Cases
- Blockchain Generations: First and Second
- Introduction to Ethereum
- Ethereum’s Decentralized Systems
- Third Blockchain Generation
- Cardano’s Native Token
- Blockchain Architecture: Layer 1
- Blockchain Types
- Evolution of the Internet
- Understanding Encryption and Decryption
- Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
- Attack Models
- Hash Function
- Avalanche Effect
- Resistance
- Types of Hash Functions
- Hash Function Applications
- Signing and Verification Algorithms in Digital Signatures
- The Digital Signature Verification Algorithm Under Attack
- Wallets in a Blockchain Network
- Hot and Cold Storage
- Introduction to Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Synchrony
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Vote-Based Consensus
- Introduction to Proof-Based Consensus
- Proof of Work
- Proof of Stake
- Different Stakeholders’ Approaches to Proof of Stake
- Proof of Authority (PoA)
- Proof of Activity (PoA)
- Proof of Importance (PoI)
- Proof of Burn (PoB)
- Proof of Capacity (PoC)/Proof of Space (PoSpace)
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)
- Proof of Contribution (PoCo)
- Proof of History (PoH)
Module 2 Overview
Builds on the concepts introduced in Module 1. It defines the transaction models used in blockchain, including account-based, Unspent Transaction Output, and extended Unspent Transaction Output. It examines the content of a block and the role of the block producer. Module 2 also explains how the risks against double-spending and Sybil attacks are mitigated, the causes of soft and hard forks, and the importance of incentive mechanisms. It concludes with a look at layer 1 and layer 2 scaling solutions.
Topics
- Introduction to Transaction Models
- Tokens
- The Transaction Lifecycle
- Record-Keeping Transaction Models
- The UTxO Transaction Model
- Inputs, Outputs and Wallets
- A Blockchain’s State
- Cardano’s Extended UTxO
- The EUTxO model
- Introduction to the Basics of Block Structure
- Longest Chain Algorithms
- Sending and Receiving Transactions via Block Producing Nodes
- Blockchain Miners
- Blockchain Parameters
- The Fundamental Properties of Blockchain
- Double-Spending Attack Example
- Block Generation Power
- Avoiding Double-Spending Attacks
- Soft Fork and Hard Fork
- Introduction to Blockchain Incentives
- Why Blockchain Needs Incentives
- Rewards in Proof-of-Work Protocols
- Types of Networks in Blockchain
- Acquiring Tokens in Mainnet and Testnet
- API and Nodes Communication Protocol
- Nebula’s Architecture
- Introduction To Scalability
- Fundamentals
- Scalability Techniques: Part 1
- Scalability Techniques: Part 2
- Scalability Techniques: Part 3
- Introduction to Layer 2 Solutions
- State Channels
- Drawbacks of State Channels
- Rollups
- Drawbacks of Rollups
- Other Scaling Solutions
Module 3 Overview
Focuses on the Cardano blockchain, it describes Cardano’s genesis and genesis entities, and the mission and principles governing Cardano. It looks at the Cardano node and how the eras have developed and enhanced features of the network. Ouroboros, Cardano’s consensus algorithm, is examined, along with the reward and incentive mechanism of Cardano. The governance process including Cardano Improvement Proposals is explained, along with the role of the Cardano Community.
Topics
- Introduction to Cardano Genesis
- Cardano’s Principles
- Cardano Genesis
- Cardano Roadmap
- Introduction to Cardano Architecture
- Cardano Eras: Part 1
- Cardano Eras: Part 2
- Networking
- Consensus in Public Permissionless Ledgers
- Ouroboros: a Family of Consensus Protocols
- The Ouroboros Family: Classic, Praos and Genesis
- Ouroboros: Crypsinous, Chronos, Leios, BFT and Omega
- Delegated Proof of Stake
- Rewards Sharing Scheme (RSS): Part 1
- Rewards Sharing Scheme (RSS): Part 2
- Wallets
- BIPs and CIPs
- Types of Addresses
- Payment Addresses
- Stake Addresses
- Fundamentals
- Programming on Cardano
- Smart Contract Languages
- Embedded Domain Specific Languages (eDSL)
- Why Does Community Matter?
- Decentralization
- What Does Community Offer?
- Why Cardano?
- Community Groups: Part 1
- Community Groups: Part 2
- History
- Cardano Improvement Proposals
- The CIP Process
- The CIP Actors
- Notable CIPs: Part 1
- Notable CIPs: Part 2
Module 4 Overview
Looks at how to get started buying, storing, and transferring ada. It also examines how staking works on Cardano with the staking lifecycle, along with the role of stake pools and stake pool operators. It describes how to create and transfer both native assets and non-fungible tokens and concludes with a look at decentralized applications and exchanges.
Topics
- Smart Contract Programming Frameworks
- API Query Layers
- Other Tools and Services
- Blockchain Explorers
- Choosing a Wallet
- Getting Started With Your Chosen Wallet
- Buying ADA from a Centralized Exchange (CEX)
- Transactions
- Staking on Cardano
- Stake Pool Operators (SPOs)
- How to Choose a Stake Pool?
- Cardano Foundation Delegation Strategy
- Alice and Bob Q&A
- Chimeric Ledger
- Staking Lifecycle: GUI vs CLI
- Jargon Buster
- Metadata Standards
- Creating a Native Token
- Wallets and DApps Interactions
- DApp Tour: Part 1
- DApp Tour: Part 2
- DApp Tour: Part 3
- Future of DApps on Cardano
- Security and Standards
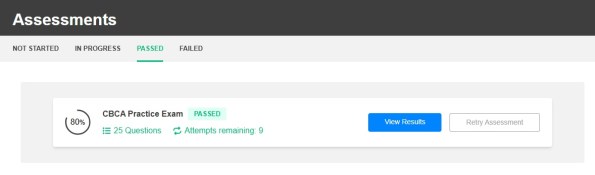
Practice Exam
Web 3.0 Procurement. Chainlink Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Chainlink Ecosystem
Chainlink is a blockchain abstraction layer that enables universally connected smart contracts. Through a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink allows blockchains to securely interact with external data feeds, events and payment methods, providing the critical off-chain information needed by complex smart contracts to become the dominant form of digital agreement.
The Chainlink Network is driven by a large open-source community of data providers, node operators, smart contract developers, researchers, security auditors and more. The company focuses on ensuring that decentralized participation is guaranteed for all node operators and users looking to contribute to the network.
Tokenized assets
Reliable and automated data integration. Attach any type of financial data to tokenized assets and automate updates to increase investor transparency and reduce manual efforts.
Automated compliance. Meet regulatory requirements and internal policies by embedding compliance solutions directly into tokenized assets.
Faster market entry with scalable infrastructure. Accelerate time-to-market and increase global access by securely connecting across any public or private blockchain with a single integration.
Enable digital asset mobility. Seamless connectivity between blockchains and traditional finance. Easily integrate traditional financial systems with blockchains to increase liquidity and market accessibility for institutions and protocols alike.
Real-time data synchronization. Keep tokenized assets updated with real-time valuations and compliance data to support seamless, real-time markets as assets move across chains.
Privacy and security for institutional transactions. Support secure, private cross-chain transactions that protect financial data while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Streamline post-trade operations. Atomic settlement. Create payment-versus-payment (PvP) and delivery-versus-payment (DvP) workflows onchain while mitigating counterparty risks.
Enhanced operational efficiency. Automate post-trade processes to reduce settlement delays, reconciliation errors, and operational costs.
Automated and efficient risk management. Add real-time risk monitoring, automated compliance, and smarter collateral management to transactions to reduce exposure as assets move from one party to another.
StableCoins
Market confidence. Enhance credibility with institutions by building on stablecoin infrastructure recognized across global capital markets for its security, reliability, and operational maturity.
Automated compliance. Support seamless regulatory compliance across jurisdictions with real-time policy enforcement, secure identity management, and streamlined monitoring and reporting.
Secure interoperability. Unlock multi-chain stablecoin distribution through Chainlink’s enterprise-grade interoperability standard, enabling greater market reach without introducing fragmentation risk.
End-to-end reliability. Prevent downtime and disruption with battle-tested infrastructure that supports stablecoin operations at scale.
Operational transparency. Ensure visibility into reserves backing stablecoins with infrastructure that makes reserve validation available onchain.
DeFi utility. Protocols and investors prefer to only list, integrate, and support assets with verifiable backing, enhancing liquidity.
Data-driven minting logic. Anchor stablecoin issuance to real-world asset values for high-integrity operations.
Proof of Reserves enforcement. Accelerate the growth of ecosystems with infrastructure designed to scale securely as networks mature.
Controlled stablecoin issuance. Enforce collateral thresholds, allowlist access, and issuance rules to ensure stablecoins are compliant.
Ecosystem liquidity unlocked. Preferred by DeFi and institutional protocols, making it easier for stablecoins to integrate into high-liquidity environments and access built-in demand.
Blockchain-agnostic movement. Facilitate stablecoin transfers across different blockchain environments with secure delivery and consistent logic.
Seamless value exchange across markets. Move stablecoins between fragmented liquidity venues and infrastructure layers without integration friction or operational overhead.
Programmable transfer logic. Embed transfer conditions directly into smart contracts to automate controls such as allowlisting, rate limits, and jurisdiction-aware routing.
Payment settlement. Use trusted exchange rates and secure messaging to settle stablecoin payments between currencies quickly and at low cost.
Interoperability with global financial infrastructure. Seamlessly settle transactions using existing payment rails, from market infrastructures to fintech platforms.
Compliance focused. Automatically apply sanctions screening, jurisdiction rules, and audit logging to stablecoin transfers at the point of settlement.
DeFi
Most decentralized and secure. Chainlink oracle networks are secured by node operators running security-audited software that has been rigorously validated to operate at scale without downtime or corruption.
Highest quality data, resistant to manipulation. Data is sourced from multiple premium, authenticated APIs that are aggregated into a final validated answer, removing any single point of failure.
Most widely adopted oracle network in DeFi. The Chainlink Network helps secure tens of billions of dollars within the DeFi ecosystem by connecting hybrid smart contracts with high-quality data and offchain computation.
Rapid integration and deployment. Developers can rapidly build, test, and deploy advanced DeFi applications that leverage multiple external resources using pre-built and reliable decentralized services.
A diverse range of decentralized services. Chainlink powers numerous decentralized services, including Data Feeds, Proof of Reserve, Automation, Verifiable Randomness Function, and Cross-Chain Interoperability.
Blockchain-agnostic oracle networks. Developers building DeFi applications have access to external data and computation across all leading smart contract-enabled blockchain networks to support multi-chain development.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Binance Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Binance Ecosystem
BNB is the native coin of the BNB Chain ecosystem, essential for powering its multifaceted Web3 environment. It supports transactions on the BNB Smart Chain (BSC), the opBNB L2s, and BNB Greenfield . Besides transaction fees, BNB serves as a governance token, granting holders the ability to participate in the BNB Chain’s decentralized on-chain governance.
Additionally, BNB functions as a strategic reserve asset and plays a critical role in the BNB Executive Total Value Locked (TVL) campaign, driving ecosystem growth and incentivizing adoption.
Real World Assets Tokenization
Real World Assets (RWAs) in crypto involve tokenizing physical assets like real estate, receivables, and loans on blockchain. Tokenizing real-world assets (RWAs) involves converting ownership rights of physical assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. It provides liquidity for your tangible assets and creates better cash flow for you.
BNB Chain Payment Solution
Still trying to figure out how to integrate BNB Chain payment gateways into your business? Still confused about where you could spend your cryptos? You come to the right place.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Avalanche Ecosystem
 Web 3.0 Procurement. Avalanche Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Avalanche Ecosystem
Avalanche is a layer one blockchain that functions as a platform for decentralized applications and custom blockchain networks. It is one of Ethereum’s rivals, aiming to unseat Ethereum as the most popular blockchain for smart contracts. It aims to do so by having a higher transaction output of up to 6,500 transactions per second while not compromising scalability.
This is made possible by Avalanche’s unique architecture. The Avalanche network consists of three individual blockchains: the X-Chain, C-Chain and P-Chain. Each chain has a distinct purpose, which is radically different from the approach Bitcoin and Ethereum use, namely having all nodes validate all transactions. Avalanche blockchains even use different consensus mechanisms based on their use cases.
After its mainnet launch in 2020, Avalanche has worked on developing its own ecosystem of DApps and DeFi. Different Ethereum-based projects such as SushiSwap and TrueUSD have integrated with Avalanche. Furthermore, the platform is constantly working on improving interoperability between its own ecosystem and Ethereum, like through the development of bridges.
Business & Consumer Applications
Avalanche accelerates blockchain business growth by enabling fast, scalable Web3 application development. The Avalanche network is a system of interconnected Layer 1 blockchains, linked through native Interchain Messaging. With built-in customizability and out-of-the-box tooling, projects on Avalanche can scale both up and across the network. Avalanche L1s offers tailored technology for real-world needs.
DeFi on Avalanche
Avalanche’s ultra-fast, low-latency network provides the building blocks for a scalable, efficient and cost-effective financial system on-chain. Avalanche supports everything from dynamic trading strategies to programmable stablecoins, while customizable Layer 1s (L1s) allow institutions to deploy tailored, compliance-aware environments.
Infrastructure on Avalanche
Avalanche is all about scalable and interoperable blockchains, facilitated by Avalanche’s native Interchain Messaging (ICM) feature. Avalanche is the multi-chain platform helping build a scalable Web3 universe—designed with precision control over execution, validation, and cross-chain interoperability. Interchain Messaging enables communication across the layer 1 multiverse for interoperability out-of-the-box.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Cardano Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Cardano Ecosystem
Cardano is a groundbreaking blockchain platform that uses proof-of-stake technology to create a more sustainable and accessible financial system. It stands out for its research-first approach and scientific philosophy, making it highly secure and energy-efficient. The platform aims to provide reliable financial services to everyone, including those currently without access to traditional banking. Since its inception, it has evolved into one of the leading blockchain platforms, processing millions of transactions while maintaining its commitment to sustainability and academic rigor.
Retail
Counterfeit goods pose a significant challenge to the global economy, causing financial losses, eroding brand reputation, and reducing customer trust. Cardano’s blockchain offers a tamper-proof solution to combat counterfeiting by providing secure, immutable systems for tracking product provenance and ensuring authenticity. Businesses can certify the originality of their products, enabling consumers to verify authenticity instantly and building confidence in the supply chain.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chains often lack transparency and efficiency, leading to counterfeit goods, poor quality control, and increased costs. Cardano’s blockchain enables real-time tracking and verification of goods. Companies can record every step of a product’s journey, from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and improving logistical processes.
Smart Contract
Cardano introduced smart contracts in 2021 and now supports the development and deployment of smart contracts using multiple different languages.
- Aiken – for on-chain validator scripts only: a language & toolchain favouring developer experience.
- Marlowe – a domain-specific language, it covers the world of financial contracts.
- opshin – a programming language for generic Smart Contracts based on Python.
- Plutus – a platform to write full applications that interact with the Cardano blockchain.
- plu-ts – Typescript-embedded smart contract programming language and a transaction creation library.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Polkadot Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Polkadot Ecosystem
Polkadot is an open-source sharded multichain protocol that connects and secures a network of specialized blockchains, facilitating cross-chain transfer of any data or asset types, not just tokens, thereby allowing blockchains to be interoperable with each other. Polkadot was designed to provide a foundation for a decentralized internet of blockchains, also known as Web3.
Polkadot is known as a layer-0 metaprotocol because it underlies and describes a format for a network of layer 1 blockchains known as parachains (parallel chains). As a metaprotocol, Polkadot is also capable of autonomously and forklessly updating its own codebase via on-chain governance according to the will of its token holder community.
Polkadot provides a foundation to support a decentralized web, controlled by its users, and to simplify the creation of new applications, institutions and services.
The Polkadot protocol can connect public and private chains, permissionless networks, oracles and future technologies, allowing these independent blockchains to trustlessly share information and transactions through the Polkadot Relay Chain (explained further down).
Polkadot’s native DOT token serves three clear purposes: staking for operations and security, facilitating network governance, and bonding tokens to connect parachains .
Smart Contract
Polkadot offers developers flexibility in building smart contracts, supporting both Wasm-based contracts using ink! (written in Rust) and Solidity contracts executed by the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine).
- Wasm (ink!) contracts – contracts are written in Rust and compiled to Wasm. The advantage of Wasm is that it allows for more flexibility, speed, and potentially lower execution costs compared to EVM, especially in the context of Polkadot’s multi-chain architecture
- EVM-compatible contracts – contracts are written in languages like Solidity or Vyper and executed by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The EVM is widely standardized across blockchains, including Polkadot parachains like Astar, Moonbeam, and Acala. This compatibility allows contracts to be deployed across multiple networks with minimal modifications, benefiting from a well-established, broad development ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Algorand Ecosystem
 Web 3.0 Procurement. Algorand Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Algorand Ecosystem
Algorand is a self-sustaining, decentralized, blockchain-based network that supports a wide range of applications. These systems are secure, scalable and efficient, all critical properties for effective applications in the real world. Algorand will support computations that require reliable performance guarantees to create new forms of trust.
DeFi
Ultra-low transaction fees and instant finality make DeFi applications on Algorand accessible and highly efficient. Algorand’s Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism offers a secure and decentralized environment for DeFi applications. Bridge assets to and from Algorand through robust interoperability solutions, connecting Algorand to other blockchains and the outside world. Algorand is scalable by design, ensuring its DeFi protocols can handle high transaction fees without compromising speed or cost.
Tokenized real-world assets
Tokenization reduces reliance on intermediaries, lowering costs and streamlining operations. Tokenization opens up investments to broader audiences, promoting financial inclusion. Blockchain ensures clear ownership and transfer history for tokenized assets. Enhanced access through tokenization drives increased liquidity, making assets easier to trade.
Data traceability & tracking solutions
Algorand’s Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism fosters a secure and decentralized environment for data traceability and tracking applications. PPoS is built to scale—meaning it can handle high transaction throughput without compromising speed or cost. Algorand’s fast block time and instant finality translate to near real-time data traceability. This ensures updates are recorded quickly and irreversibly, offering a secure and trustworthy audit trail for tracked information. Algorand’s low transaction fees make it suitable for scenarios where frequent data tracking is required. This may be ideal for applications like supply chain management, where every step of a product’s journey needs to be documented.
Stablecoins, digital money & payment solutions
Transaction fees on Algorand are incredibly low at 0.001 Algo per transaction, making it a viable option for everyday purchases and microtransactions. Stablecoins on Algorand are accessible to all, even those without a bank account. Anyone in the world can set up a mobile crypto wallet and gain access. Algorand users can transact with price-stable assets, lowering cryptocurrency volatility concerns. Algorand’s Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism delivers a secure and decentralized environment for digital money and payment solutions. Algorand is scalable by design, ensuring applications can handle high transaction volume without compromising speed or cost. With custom smart contract support, Algorand enables developers to build innovative payment solutions and integrate them seamlessly with existing systems.
Smart Contracts
Algorand Smart Contracts (ASC1) are self-executing programs deployed on the Algorand blockchain that enable developers to build secure, scalable decentralized applications. Smart contracts on Algorand can be written in Algorand Typescript, Algorand Python, or directly in TEAL. Smart contract code written in Typescript or Python is compiled to TEAL, an assembly-like language that is interpreted by the Algorand Virtual Machine (AVM) running within an Algorand node.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Solana Ecosystem
 Web 3.0 Procurement. Solana Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Solana Ecosystem
Solana is a highly functional open source project that banks on blockchain technology’s permissionless nature to provide decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions. The Solana protocol is designed to facilitate decentralized app (DApp) creation. It aims to improve scalability by introducing a proof-of-history (PoH) consensus combined with the underlying proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus of the blockchain. Because of the innovative hybrid consensus model, Solana enjoys interest from small-time traders and institutional traders alike. A significant focus for the Solana Foundation is to make decentralized finance accessible on a larger scale.
Smart Contract
On Solana, “smart contracts” are called programs. Programs are deployed on-chain to accounts that contain the program’s compiled executable binary. Users interact with programs by sending transactions containing instructions that tell the program what to do.
Solana programs are predominantly written in the Rust programming language, with two common approaches for development:
Anchor: A framework designed for Solana program development. It provides a faster and simpler way to write programs, using Rust macros to reduce boilerplate code. For beginners, it is recommended to start with the Anchor framework.
Native Rust: This approach involves writing Solana programs in Rust without leveraging any frameworks. It offers more flexibility but comes with increased complexity.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Ethereum Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Ethereum Ecosystem
Ethereum is a decentralized open-source blockchain system that features its own cryptocurrency, Ether. ETH works as a platform for numerous other cryptocurrencies, as well as for the execution of decentralized smart contracts.
Ethereum’s own purported goal is to become a global platform for decentralized applications, allowing users from all over the world to write and run software that is resistant to censorship, downtime and fraud.
DeFi
DeFi is an open and global financial system built for the internet age – an alternative to a system that’s opaque, tightly controlled, and held together by decades-old infrastructure and processes. It gives you control and visibility over your money. It gives you exposure to global markets and alternatives to your local currency or banking options. DeFi products open up financial services to anyone with an internet connection and they’re largely owned and maintained by their users. So far tens of billions of dollars worth of crypto has flowed through DeFi applications and it’s growing every day.
DAO
A DAO is a collectively-owned organization working towards a shared mission. DAOs allow us to work with like-minded folks around the globe without trusting a benevolent leader to manage the funds or operations. There is no CEO who can spend funds on a whim or CFO who can manipulate the books. Instead, blockchain-based rules baked into the code define how the organization works and how funds are spent. They have built-in treasuries that no one has the authority to access without the approval of the group. Decisions are governed by proposals and voting to ensure everyone in the organization has a voice, and everything happens transparently onchain.
Payments
While traditional financial institutions have built robust payment systems over decades, they often remain constrained by borders, working hours, and legacy infrastructure. Ethereum offers a new paradigm: a global, 24/7 financial platform that enables near-instant, programmable transactions for anyone with internet access.
Smart contract
A “smart contract” is simply a program that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. It’s a collection of code (its functions) and data (its state) that resides at a specific address on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts are a type of Ethereum account. This means they have a balance and can be the target of transactions. However they’re not controlled by a user, instead they are deployed to the network and run as programmed. User accounts can then interact with a smart contract by submitting transactions that execute a function defined on the smart contract. Smart contracts can define rules, like a regular contract, and automatically enforce them via the code. Smart contracts cannot be deleted by default, and interactions with them are irreversible.
The two most active and maintained languages are:
Solidity
- Object-oriented, high-level language for implementing smart contracts.
- Curly-bracket language that has been most profoundly influenced by C++.
- Statically typed (the type of a variable is known at compile time).
- Supports: Inheritance, Libraries, Complex user-defined types.
Vyper
- Pythonic programming language
- Strong typing
- Small and understandable compiler code
- Efficient bytecode generation
- Deliberately has less features than Solidity with the aim of making contracts more secure and easier to audit.
Smart Contract. Product Management
Smart Contract. Product Management
08.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Product Management
Code
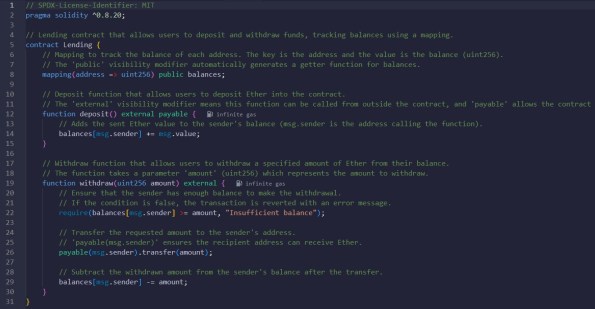
Smart Contract. Lending
Smart Contract. Lending
07.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Lending
Code
Smart Contract. Payment Channel
Smart Contract. Payment Channel
06.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Payment Channel
Code

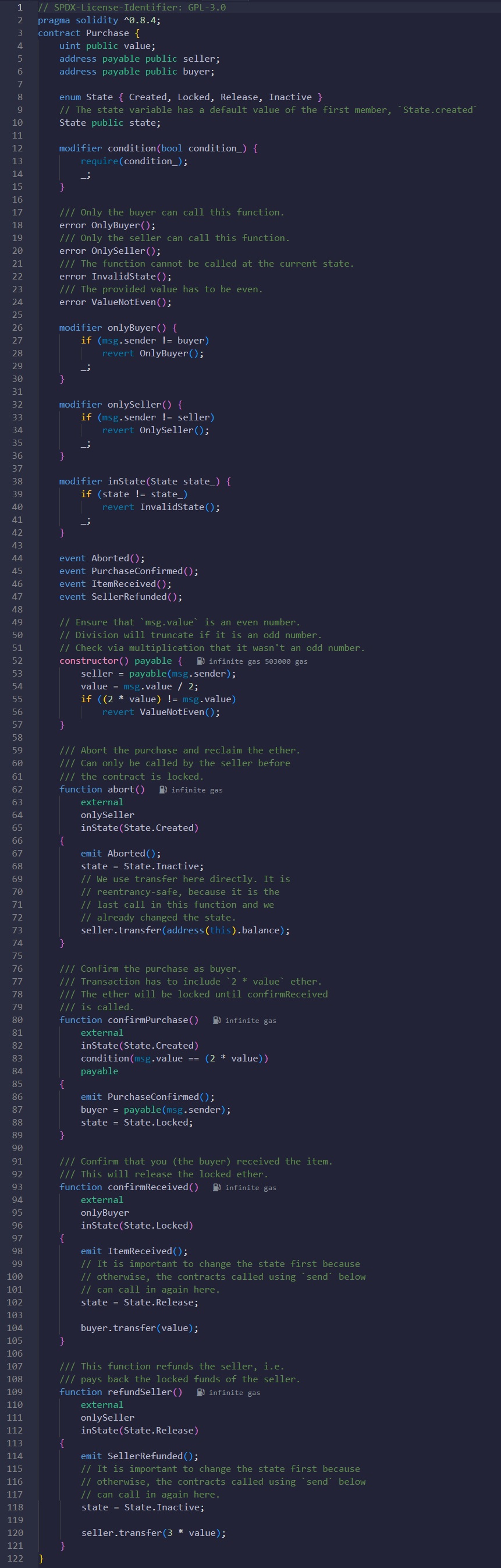
Smart Contract. Remote Purchase
Smart Contract. Remote Purchase
05.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Remote Purchase
Code
Smart Contract. English Auction for Tender Procedure
Smart Contract. English Auction for Tender Procedure
04.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for English Auction for Tender Procedure
Code

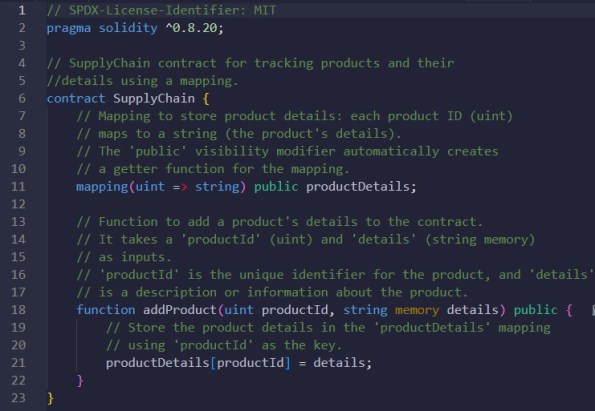
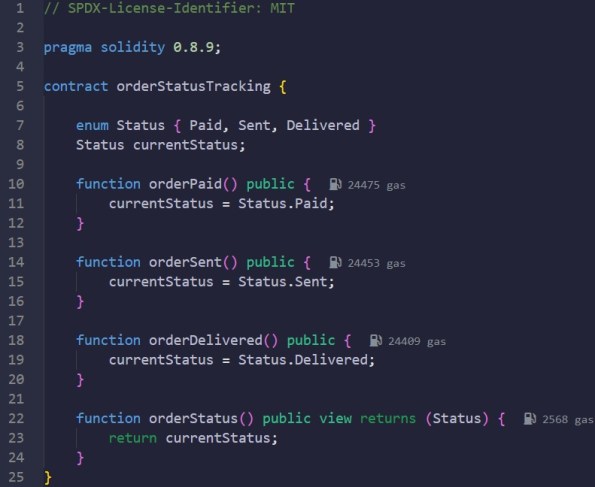
Smart Contract. Order Status Tracking
Smart Contract. Order Status Tracking
03.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Order Status Tracking
Code
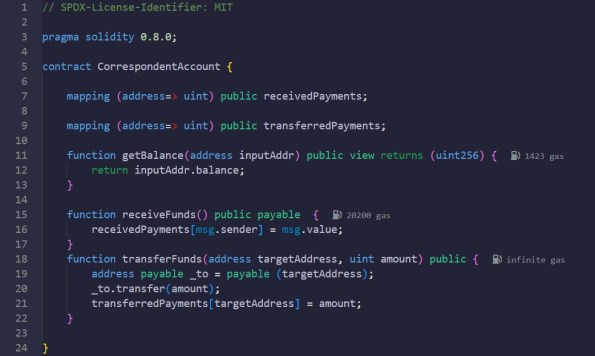
Smart Contract. Correspondent Account
 Smart Contract. Correspondent Account
Smart Contract. Correspondent Account
02.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Correspondent Account
Code
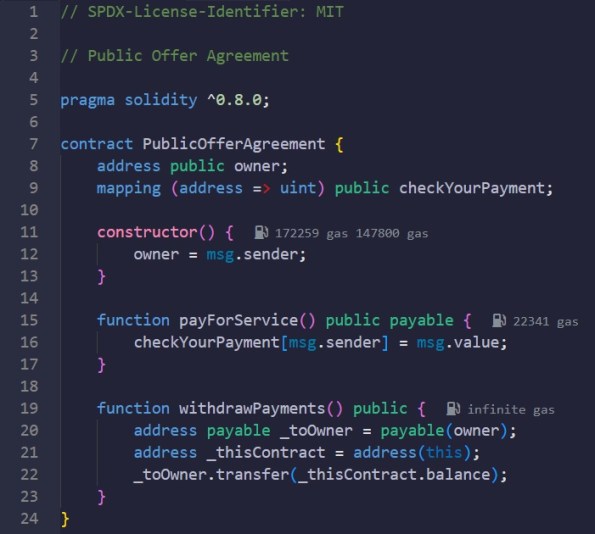
Smart Contract. Public Offer Agreement
Smart Contract. Public Offer Agreement
01.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart Contract for Public Offer Agreement
Code
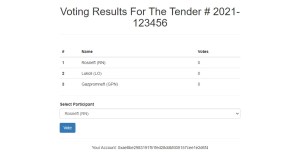
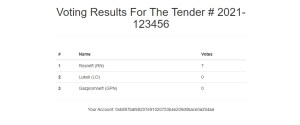
Solidity Project: Tender Voting
Project: Tender Voting
18.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: The application allows members of the tender committee to vote for the winner when evaluating participants. Such voting is open and immutable.
Results
Solidity Project: Improvement Stage
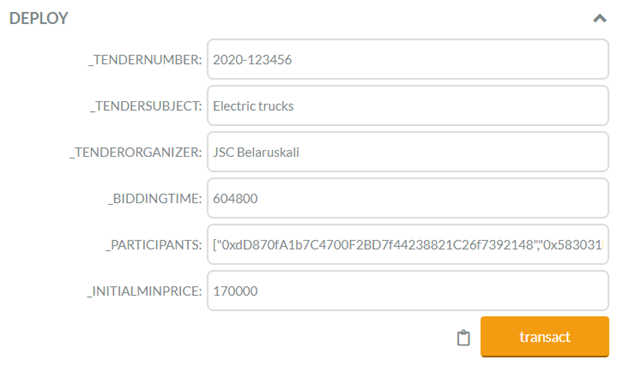
Project: Improvement Stage
17.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
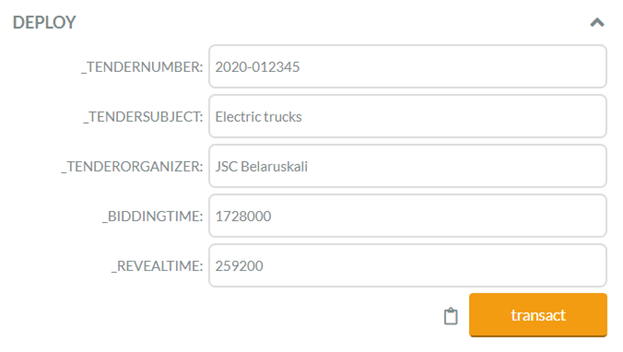
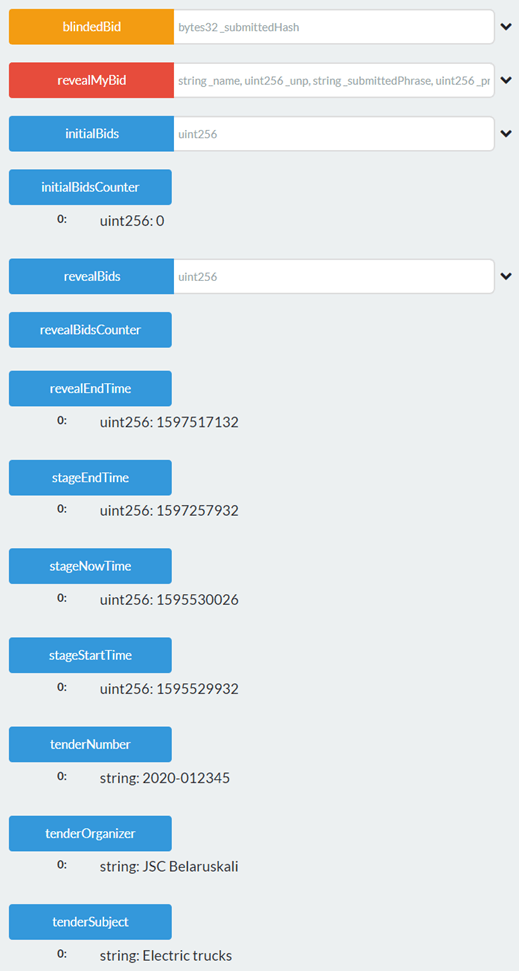
Description: Smart contract allows you to initiate Improvement Stage of the tender on the Blockchain network and submit improved commercial proposals.
Smart Contract

Screens
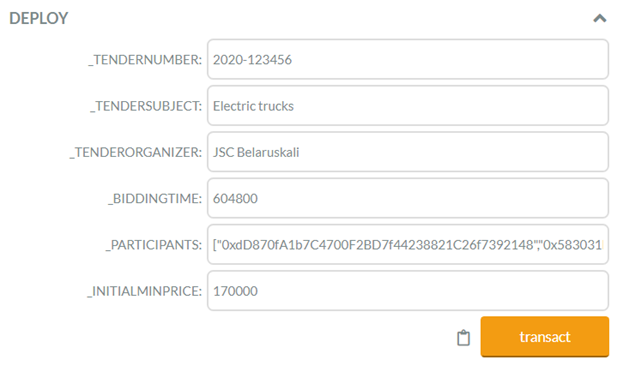



Solidity Project: Submitting Initial Commercial Offers
 Project: Submitting Initial Commercial Offers
Project: Submitting Initial Commercial Offers
16.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
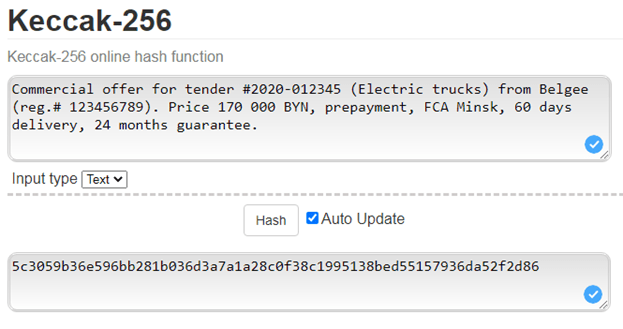
Description: Smart contract allows you to initiate a tender on the Blockchain network and submit initial commercial proposals.
Smart Contract

Screens

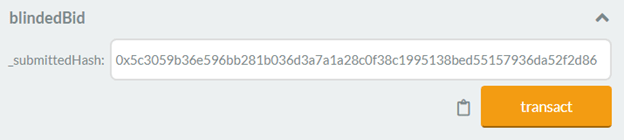

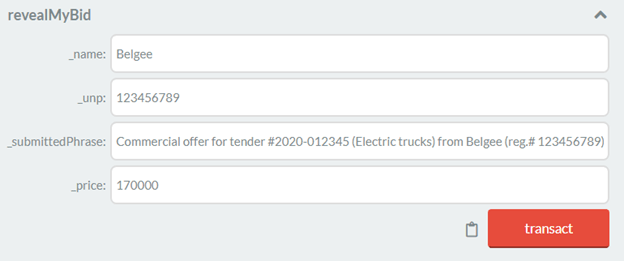
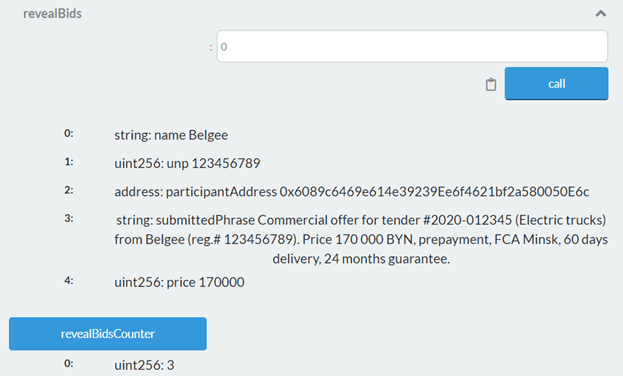
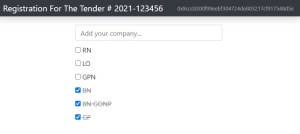
Solidity Project: Registration For The Tender
Project: Registration For The Tender
15.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: The application allows you to register all companies to participate in the specified tender. Such registration is open and immutable. Then the specialist of the tender can eliminate the participants who did not send commercial offers.
Results
Training.eos.io Platform

Eos.io
via Training.eos.io Platform
06.02.2020
Online Educational Course “Smart Contracts 201”
The content of the modules:
Module 1: Assets
- Introduction to tokens
- The eosio.token contract
- The asset type
Module 2: Receiving Transfers
- on_notify, especially [[eosio::on_notify(“eosio.token::transfer”)]]
- The old way: custom apply()
Module 3: In-line Actions
- Review of the eosio.code permission
- require_recipient()
- Explanation of why we must use require_auth(get_self()) with require_recipient()
- <action type>.send(…), the action constructor (permission, action, data)
- Action wrappers
- Custom permissions
Module 4: Singletons
- Appropriate for single-row use cases, such as contract settings
- Using get() and set()
Module 5: Bonus Lab: Add a “Pot” to Tic Tac Toe Games
Module 6: Updating Table Schemas and Migrating Data
- Review of inability to update structure of contract table containing data
- Description of migration options, including the binary_extension wrapper
Module 7: Getting Data from the Outside World
- The Oracle Problem
- Potential exploits (frontrunning, collusion, etc.)
- Delphi
- Provable
- Native EOSIO Oracles
- LiquidOracles
Module 8: Organizing Action Parameters
- Action parameter list organization and serializiation
- Situations requiring packed parameters
Module 9: Randomness
- Recap of the need for determinism in blockchains
- Pseudo-randomness and its dangers
- Multi-party randomness
- Oracle-based randomness
Module 10: Scheduled and Recurring Actions
- Deprecated: deferred transactions
- Provable, LiquidOracles, and other methods for scheduling actions
- Using contract design to mitigate the need for scheduled actions
Module 11: User-Friendly Resource Management
- RAM Payer
- ONLY_BILL_FIRST_AUTHORIZER
Module 12: More to Explore: Interoperability and Testing Frameworks
- Intro to interoperability/IBC
- Survey of testing tools available for EOSIO smart contracts
Training.eos.io Platform

Eos.io
via Training.eos.io Platform
05.02.2020
Online Educational Course “Smart Contracts 101”
The content of the modules:
- Module 0: Survey of Prerequisite Knowledge
- Module 1: Smart Contracts on EOSIO
- Module 2: Getting Started with Smart Contract Development
- Module 3: Persistence with Multi-Index Tables
- Module 4: Secondary Indices
- Module 5: The ABI
- Module 6: Building Out Tic Tac Toe
- Module 7: Reading and Debugging EOSIO Code
- Module 8: Final Project
Project
Chainshot.com Platform

Chainshot by Alchemy
via Chainshot.com Platform
04.02.2020
Online Educational Course “Introduction to Solidity”
The content of the modules:
- Welcome to ChainShot. An Introduction to Learning with ChainShot
- Getting Started. Tips & Guides for Getting Started on your Journey
- Curriculum & Resources. Learn about the curriculum and discover some useful resources
- Understanding Solidity. Learn the Fundamentals of Solidity
- Solidity at a Glance. A Look at the Solidity Language from a Beginner’s Perspective
- Data Types. Learn the Basic Solidity Data Types
- Functions. Learn the Syntax of Writing Functions in Solidity
- Contract Communication. Learn to Communicate Between Contracts
- Libraries. DRY up your code with Solidity Libraries
- Addresses & Accounts. Learn about the address data type and Solidity execution context
- Contract to Contract. Learn how to communicate between contracts
- Events. Defining and Emitting Contract Events
- Solidity Challenges. Test Your Skills!
- Sum and Average. Can you find the sum and average of the arguments?
Project
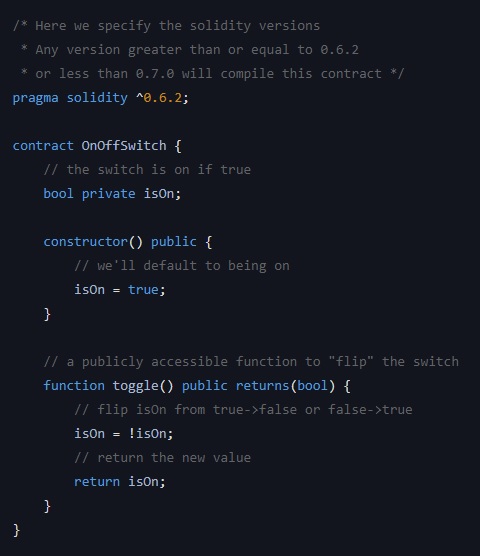
Web3.university Platform

Web3.university
via Web3.university Platform
03.02.2020
Online Educational Course “How To Create Your First Smart Contract”
The content of the modules:
- What are Smart Contracts?
- Deploy Your First Smart Contract
- What is Gas and How is it Used?
- Interact With Your Smart Contract
- Structure of a Smart Contract
- Submit Your Smart Contract to Etherscan
- Smart Contract Security Challenges
- Integrate Your Contract With a Frontend
- Additional Resources
Project
Hello World smart contract from the Ethereum Foundation
// Specifies the version of Solidity, using semantic versioning.
// Learn more: https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/v0.5.10/layout-of-source-files.html#pragma
pragma solidity >=0.7.3;
// Defines a contract named `HelloWorld`.
// A contract is a collection of functions and data (its state). Once deployed, a contract resides at a specific address on the Ethereum blockchain. Learn more: https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/v0.5.10/structure-of-a-contract.html
contract HelloWorld {
//Emitted when update function is called
//Smart contract events are a way for your contract to communicate that something happened on the blockchain to your app front-end, which can be 'listening' for certain events and take action when they happen.
event UpdatedMessages(string oldStr, string newStr);
// Declares a state variable `message` of type `string`.
// State variables are variables whose values are permanently stored in contract storage. The keyword `public` makes variables accessible from outside a contract and creates a function that other contracts or clients can call to access the value.
string public message;
// Similar to many class-based object-oriented languages, a constructor is a special function that is only executed upon contract creation.
// Constructors are used to initialize the contract's data. Learn more:https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/v0.5.10/contracts.html#constructors
constructor(string memory initMessage) {
// Accepts a string argument `initMessage` and sets the value into the contract's `message` storage variable).
message = initMessage;
}
// A public function that accepts a string argument and updates the `message` storage variable.
function update(string memory newMessage) public {
string memory oldMsg = message;
message = newMessage;
emit UpdatedMessages(oldMsg, newMessage);
}
}Learn.microsoft.com Platform

Microsoft
via Learn.microsoft.com Platform
01.02.2020
Online Educational Course “Write Ethereum smart contracts by using Solidity”
The content of the modules:
- Introduction
- What is a smart contract?
- Exercise – Install Truffle
- Exercise – Install the Truffle for VS Code extension
- Exercise – Write a smart contract
- Exercise – Test your smart contract
- Knowledge check
- Summary
Project

Learn.microsoft.com Platform

Microsoft
via Learn.microsoft.com Platform
01.02.2020
Online Educational Course “Learn how to use Solidity”
The content of the modules:
- Introduction
- What is Solidity
- Understand the language basics
- Explore value types
- Explore reference types
- Exercise – Write your first contract
- Knowledge check
- Summary
Project